What Is THCP?
Written By QuickMedCards. Reviewed by Dr. Shatha Atiya, PsyD. Updated November 10, 2025
Imagine a cannabinoid that’s potentially 33 times stronger than regular THC. That’s tetrahydrocannabiphorol, or rather THCP.
Discovered in 2019, this new cannabinoid has caught the attention of researchers, consumers, and the hemp industry.
Here’s what makes THCP different: it latches onto your brain’s CB1 receptors much more tightly than delta-9 THC. That’s the compound that gets you high in regular cannabis. Lab tests show this tight grip could mean powerful effects. Even so, human data is scarce, and real‑world impacts are still under investigation.
This article will walk you through what THCP is, how it compares to other types of THC, and what the early research shows. Moreover, it’ll prepare you before using any THCP product.
By the end of this page, you will have the answers to these questions:
- What is THCP, and how was it discovered?
- How strong is THCP?
- What are the potential THCP benefits?
- What are the THCP side effects?
- Is THCP legal?
- What are the best THCP products?
- What is the difference between THC and THCP?
Looking for a Medical Marijuana Doctor?
What’s THCP?
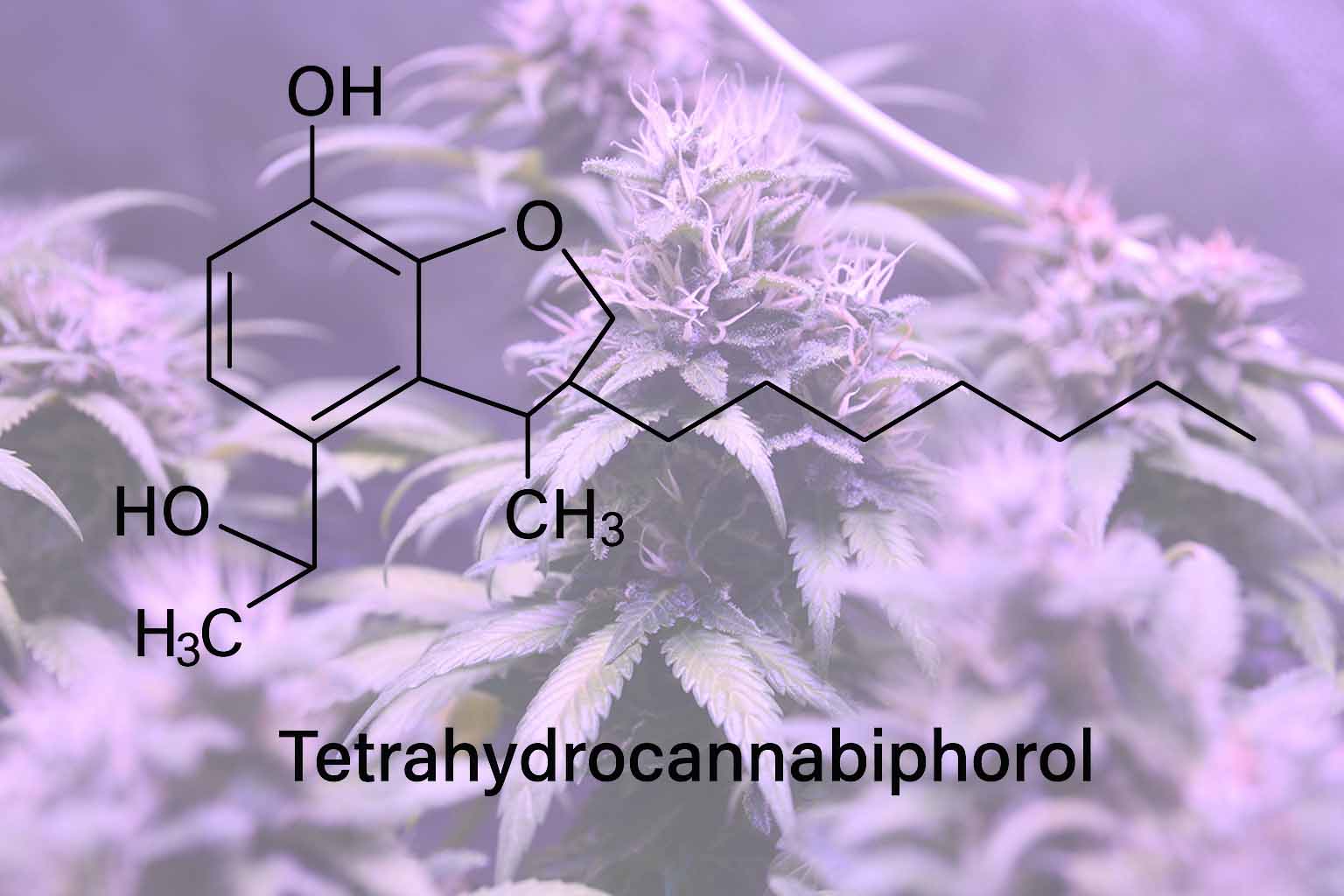
THCP (Δ9‑tetrahydrocannabiphorol) is a naturally occurring cannabinoid identified in 2019. THCP has a seven-carbon side chain. That is two more than Delta 9 THC. As a result, it has a much higher affinity for CB1 receptors and potentially stronger psychoactive effects at smaller doses.
You won’t find much THCP in nature, as cannabis plants produce it only in trace amounts. That’s why most commercial THCP products start with hemp and use chemical synthesis to create the final compound.
Users report pronounced euphoria, altered perception, and deep body relaxation. But some experience anxiety, dizziness, or rapid heartbeat instead.
You’ll find THCP in vape cartridges, tinctures, and edibles. Each form kicks in at different speeds and lasts for various lengths of time.
Is THCP dangerous? Well, quality varies widely across products. So, always look for third‑party lab reports. These should verify what’s actually in the product, its potency, and whether it contains contaminants.
A brief history of discovery
In late 2019, an Italian team studied the FM2 cannabis chemovar. They used ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography and isolated two new cannabinoids, THCP and CBDP. They published the work in Scientific Reports and named the compound (-)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabiphorol (Delta-9-THCP).
The tests showed THCP binds very strongly to CB1 and CB2 receptors. That finding widened the cannabinoid map and nudged researchers to explore other long-chain analogs.
How Strong is THCP?
THCP potency in humans depends on multiple factors beyond receptor binding, which include:
- Bioavailability: How much of the cannabinoid reaches circulation.
- Metabolism: How quickly the liver converts THCP into other molecules.
- Functional efficacy: How well binding translates into downstream cellular action.
- Individual variability: Includes genetics, tolerance, and concurrent medications.
No peer-reviewed human trials have yet quantified THCP’s psychoactive intensity or therapeutic window. Anecdotal reports describe a rapid onset followed by 4 to 6 hours of pronounced euphoria, analgesia, and, in some cases, dizziness or sedation. Until standardized studies emerge, claims that THCP is “33 times stronger” remain theoretical.
THCP Benefits
Pain and inflammation
Cannabinoids with high CB1 affinity often reduce neuropathic pain in animal models. Preclinical studies hint that THCP may activate CB1-mediated analgesic pathways more efficiently than THC, but no published animal or human pain trials exist.
Appetite stimulation
Rodent assays cited in the original study noted increased feeding after THCP administration, aligning with CB1 involvement in appetite regulation. If confirmed in humans, THCP could someday aid patients with cancer or HIV-related wasting.
Nausea control
THCP’s strong CB1 activity theoretically supports antiemetic effects, yet direct evidence is absent. Standard medications or THC-based pharmaceuticals such as dronabinol remain the best-studied options.
Mood and sleep
High-affinity CB1 agonists can elevate mood at low doses and promote sleep at higher doses. Patient anecdotes point to profound relaxation, though some users report anxiety at excessive intakes. Personalized dosing and medical supervision are advisable.
THCP Side Effects
THCP side effects can be stronger than regular THC, especially for new users. So, knowing what THCP does and how it affects your body matters before your first dose.
Intensified psychoactivity
Because THCP may cross the blood-brain barrier efficiently, beginners risk overconsumption. Reported side effects mirror high-dose THC: rapid heart rate, dry mouth, short-term memory impairment, and anxiety.
Limited safety data
No chronic toxicity, reproductive, or carcinogenicity studies have been published. Without these, long-term safety remains unknown.
Drug interactions
Like THC, THCP is likely metabolized by CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 enzymes. Co-administration with warfarin, certain anticonvulsants, or macrolide antibiotics might raise plasma levels of either drug, although interactions have not been formally measured.
Impairment and driving
Due to its putative potency and extended duration, patients should avoid driving or operating machinery after THCP use until they understand their individual response.
Is THCP Legal?
Is THCP legal? The answer isn’t simple. THCP sits in a gray area between hemp and synthetic cannabinoids. While the 2018 Farm Bill opened doors for hemp derivatives, THCP’s legal status still depends on how and where it’s made and where you live.
Federal overview
Under the 2018 Farm Bill, cannabinoids derived from hemp containing less than 0.3 percent delta-9 THC by dry weight are not scheduled under the Controlled Substances Act. Manufacturers argue that hemp-converted THCP products qualify. However, the DEA clarifies that synthetic cannabinoids structurally related to THC may still be Schedule I, regardless of delta-9 content.
State-level regulations
Several states, including Colorado and New York, have moved to restrict or ban intoxicating hemp derivatives such as delta-8. THCP falls into the same gray zone. Patients should review state regulations or ask licensed cannabis counsel before purchasing.
Lab testing challenges
Most commercial labs do not yet differentiate THCP from THC on routine panels, making accurate potency labeling difficult. Consumers should seek certificates of analysis that specifically list “Δ9-THCP” concentrations.
How is THCP Made?
How is THCP made if cannabis plants barely produce it? Most THCP products on shelves today come from a lab, not a plant.
Natural abundance is minuscule
THCP occurs in cannabis at microgram levels, far too low for commercial extraction. To meet consumer demand, processors typically:
- Isolate CBD from legal hemp.
- Convert CBD to delta-9 THC via acid catalysis.
- Extend the alkyl side chain to produce THCP through homologation chemistry.
While legal under some interpretations of the Farm Bill, this synthetic route raises questions about purity and by-products.
THCP Products
THCP products are changing how people experience cannabinoids. Once found only in trace amounts, THCP is now available in many forms.
THCP gummies and edibles deliver a slow, steady high that builds over time. They’re ideal for longer-lasting relief.
THCP vapes and carts hit faster, offering quick effects that fade sooner. THCP flower gives a familiar smoking experience.
Meanwhile, THCP concentrates like dabs, distillate, and wax cater to those who prefer potent, refined options.
Here’s the problem, though. Most of these products skip proper testing. Therefore, always check third-party lab tests for purity, potency, and contaminants before buying.
THCP vs THC
Delta-9 THC features a five-carbon alkyl side chain. Meanwhile, THCP carries a seven-carbon side chain, allowing deeper insertion into the CB1 receptor pocket. In vitro binding assays show:
- Ki for THCP at CB1: 1.2 nM
- Ki for THC at CB1: 40 nM
A lower Ki means tighter binding, which under controlled lab conditions equates to roughly 33 times greater affinity. However, receptor affinity is only one piece of the potency puzzle.
Delta-9 THC
- Alkyl side chain: 5 carbons
- Receptor binding: Baseline
- Legal status: Federally Schedule I (except Rx)
- Research depth: Decades of data
Delta-8 THC
- Alkyl side chain: 5 carbons
- Receptor binding: Approximately two-thirds of delta-9
- Legal status: Hemp gray zone
- Research depth: Limited
THCP
- Alkyl side chain: 7 carbons
- Receptor binding: 33 times tighter (in vitro)
- Legal status: Hemp gray zone, uncertain
- Research depth: Very limited
THCP Dosing for Patients
THCP dosage guidelines don’t exist yet, and THCP overdose is easy when potency is this high. Smart THCP dosing means starting with a THCP dose far lower than you’d use for regular THC.
- Start extremely low. Given the lack of human data, 0.5 to 1 mg THCP orally or 1 to 2 inhalations is prudent for first timers.
- Wait and reassess. Onset may be fast, but peak effects can build for one to two hours orally.
- Keep a journal. Note time, dose, symptom relief, and side effects to guide titration.
- Consult professionals. Work with a cannabis-experienced clinician when adding potent new cannabinoids to your regimen.
Conclusion
THCP represents a new frontier in cannabinoid science. But the lack of human research means you’re navigating uncharted territory.
If you’re interested in exploring cannabinoids safely, consider getting a medical marijuana card. It gives you access to regulated, medical-grade products and guidance from licensed medical marijuana doctors who understand dosing and safety.
Quick Med Cards offers cheap medical marijuana cards through a simple process:
- Fill out our questionnaire form.
- Book an appointment with one of our medical marijuana doctors.
- Attend your consultation.
- Get certified for medical marijuana.
- Apply with your state’s program if required.
- Receive your medical marijuana card.
You’ll skip the gray-market guesswork and gain access to products with real oversight.
Your health deserves more than trial and error.
Key Takeaways
- THCP was discovered in 2019 by Italian researchers studying cannabis strain FM2.
- Tetrahydrocannabiphorol binds to CB1 receptors up to 33 times more tightly than delta-9 THC, suggesting stronger effects at smaller doses.
- Natural THCP exists only in trace amounts, so commercial products are synthesized from hemp-derived CBD.
- Reported THCP effects include euphoria, relaxation, and altered perception, but also anxiety and dizziness in some users.
- THCP benefits may include pain relief, appetite boost, and improved sleep, though human research is still limited.
- THCP side effects can be more intense than THC, and long-term safety data are lacking.
- The legal status of THCP sits in a gray area between hemp laws and synthetic cannabinoid restrictions.
- THCP dosing requires caution; even tiny amounts can be powerful, and overdosing is easy without proper guidance.
- Always check third-party lab reports to confirm purity, potency, and safety before trying any THCP product.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to common questions about tetrahydrocannabiphorol (THCP).
Is THCP safe?
Because long-term studies are insufficient, no one can definitively claim THCP is safe. Short-term user reports suggest side effects similar to high-dose THC. Approach cautiously and under medical guidance.
Will THCP show up on a drug test?
Standard workplace panels look for THC metabolites that THCP likely shares. A positive result is possible, especially because current assays do not distinguish the two compounds.
Can THCP help with chronic pain where THC failed?
Possibly, due to its higher CB1 affinity, but no clinical trials have confirmed superiority. Patients who did not respond to THC should not expect guaranteed success with THCP.
How do I know if a product truly contains THCP?
Ask for a certificate of analysis listing “Δ9-THCP” with an exact milligram amount. Reputable brands will provide batch-specific lab results.
Do I need a medical marijuana card to buy THCP?
In many states, hemp-derived THCP products are sold online without a card, but rules vary. Holding a state medical card often grants access to better-regulated dispensary products and medical oversight.
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical or legal advice. Cannabis affects individuals differently. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider before starting or changing any cannabinoid regimen. State and federal laws on cannabis are subject to change; check current regulations in your jurisdiction.
Get Your Medical Marijuana Card
Same-day appointments available for online medical marijuana evaluation.
Get your certification now!
